Planned Pregnancy and Weaning Celexa Help
If a woman is taking an antidepressant such as Celexa and is planning on becoming pregnant, she may want to get off Celexa and consider Celexa alternatives well before the time of conception. While many “authorities” in proximity to (and likely financially supported by) the drug industry may say that taking drugs during pregnancy is considered relatively safe, there are statistics that show a connection between antidepressants and a doubling or even tripling of frequency in birth defects in the baby, as well as postpartum hemorrhage or other complications in the mother.5 In general, studies document that Celexa is linked to adverse effects relating to the coagulation of the blood, which would remain a concern if planning a pregnancy or for many other health reasons.6
A cursory search on the topic of SSRIs and birth defects will produce much information, some of which may be confusing and contradictory. One would be well advised to search carefully through all possible unbiased literature for oneself, to make a decision regarding getting off Celexa, or other prescription medications prior to pregnancy. A properly done Celexa tapering prior to pregnancy may be considerably less risky than attempting withdrawal from Celexa during pregnancy. Before trying to quit Celexa, seek competent medical advice from a trusted and knowledgeable prescriber.
SPECIAL WARNING RE: Trying to Quit Celexa
Please be aware that the FDA advises against abrupt or sudden Celexa tapering methods.6 If you are considering trying to quit Celexa or any SSRI drug, this should only be attempted with proper preparation, education, guidance, and medical oversight in place.
Celexa Tapering Help
 At Alternative to Meds Center, many therapeutic aids are available to help ease the tapering process. Some examples are therapeutic massage, diet modification, colon hydrotherapy, nebulized glutathione, neurotransmitter rehabilitation, neurotoxin removal, counseling, Qi Gong, IV + NAD, yoga, and much more. Please see our services overview pages for more information on these and other services.
At Alternative to Meds Center, many therapeutic aids are available to help ease the tapering process. Some examples are therapeutic massage, diet modification, colon hydrotherapy, nebulized glutathione, neurotransmitter rehabilitation, neurotoxin removal, counseling, Qi Gong, IV + NAD, yoga, and much more. Please see our services overview pages for more information on these and other services.
Please contact us at Alternative to Meds Center for information that you may be searching for regarding how to get off Celexa safely and gradually. Clearly, the more information one can acquire on the subject, the better one will be equipped for a successful outcome.
Alternative to Meds Center makes its prime focus tapering medications safely and under medical oversight, with a full roster of fully licensed practitioners and clinicians who are well versed in helping our clients overcome barriers such as physical or mental discomfort during medication tapering programs We are the leading authority on safe Celexa tapering help, delivered in an exceptionally comfortable and luxurious in-patient setting.
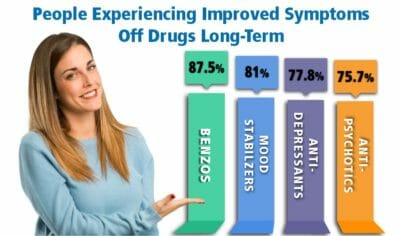
 Drugmakers downplay the addictive properties of Celexa and other antidepressants. After years of being confronted with “withdrawal reaction” evidence, have instead opted to use the softer term “discontinuation syndrome.”7 Prescribers are mandated to disclose these withdrawal reactions as part of informed consent.8 But rarely do our patients report that they recall hearing about discontinuation syndrome at the time of prescribing. Many of our patients report that if it were explained to them the addictive mechanisms of antidepressant drugs, or what might be expected when stopping Celexa, they would have rejected the medication. Unfortunately, the medical profession has little to no expertise for people who decide to come off these drugs — “no scientifically backed guidelines, no means to determine who’s at highest risk, no way to tailor appropriate strategies to individuals.”9 It is also a measure of our experience at Alternative to Meds Center that most of our patient’s former providers have little in the way of practical guidance regarding Celexa tapering methods or what to expect during Celexa cessation. In fact, many of our referrals come from these prescribers who at times feel blindsided by their patient’s withdrawal symptoms or what to do to help them.
Drugmakers downplay the addictive properties of Celexa and other antidepressants. After years of being confronted with “withdrawal reaction” evidence, have instead opted to use the softer term “discontinuation syndrome.”7 Prescribers are mandated to disclose these withdrawal reactions as part of informed consent.8 But rarely do our patients report that they recall hearing about discontinuation syndrome at the time of prescribing. Many of our patients report that if it were explained to them the addictive mechanisms of antidepressant drugs, or what might be expected when stopping Celexa, they would have rejected the medication. Unfortunately, the medical profession has little to no expertise for people who decide to come off these drugs — “no scientifically backed guidelines, no means to determine who’s at highest risk, no way to tailor appropriate strategies to individuals.”9 It is also a measure of our experience at Alternative to Meds Center that most of our patient’s former providers have little in the way of practical guidance regarding Celexa tapering methods or what to expect during Celexa cessation. In fact, many of our referrals come from these prescribers who at times feel blindsided by their patient’s withdrawal symptoms or what to do to help them. Patients are typically advised that Celexa will raise the patient’s serotonin levels, and that will fix their depressed state. They are often told of a chemical imbalance as being the cause of their depression. And while there may be some connection between brain chemicals and mood disturbances, researchers are lacking evidence to provide the optimum `balance` or clinical evidence to support the claim. 10 Persons might also be told that what they are experiencing while getting off Celexa is a “relapse” of their depression or other “mental illness” when in all actuality the discontinuation effect may be a completely different mechanism.11 Typically, there is a point of differentiation to distinguish Celexa discontinuation syndrome from a depressive relapse. Discontinuation effects will usually occur within days to a week of reducing or stopping the medication and they tend to lessen or resolve over the next 3 or so weeks. A depressive symptomatic relapse tends to occur more slowly and can get increasingly worse over time.11 If your doctor is not differentiating the two, it may help if you bring up the concept of Celexa discontinuation syndrome. If they are not able to give you guidance in distinguishing the differences, it would be wise to get a second opinion.
Patients are typically advised that Celexa will raise the patient’s serotonin levels, and that will fix their depressed state. They are often told of a chemical imbalance as being the cause of their depression. And while there may be some connection between brain chemicals and mood disturbances, researchers are lacking evidence to provide the optimum `balance` or clinical evidence to support the claim. 10 Persons might also be told that what they are experiencing while getting off Celexa is a “relapse” of their depression or other “mental illness” when in all actuality the discontinuation effect may be a completely different mechanism.11 Typically, there is a point of differentiation to distinguish Celexa discontinuation syndrome from a depressive relapse. Discontinuation effects will usually occur within days to a week of reducing or stopping the medication and they tend to lessen or resolve over the next 3 or so weeks. A depressive symptomatic relapse tends to occur more slowly and can get increasingly worse over time.11 If your doctor is not differentiating the two, it may help if you bring up the concept of Celexa discontinuation syndrome. If they are not able to give you guidance in distinguishing the differences, it would be wise to get a second opinion. The majority of these studies were never publicly released. This is sometimes called “cherry-picking” in drug trials.12
The majority of these studies were never publicly released. This is sometimes called “cherry-picking” in drug trials.12 A typical experience of antidepressant users is that either the drugs didn’t work at all, or that they caused unsustainable discomfort and intolerable symptoms, also called side effects.18 Some of the more common side effects of Celexa include:
A typical experience of antidepressant users is that either the drugs didn’t work at all, or that they caused unsustainable discomfort and intolerable symptoms, also called side effects.18 Some of the more common side effects of Celexa include: Take it slow, unless there is an urgent medical reason for immediate cessation.6
Take it slow, unless there is an urgent medical reason for immediate cessation.6 At Alternative to Meds Center, many therapeutic aids are available to help ease the tapering process. Some examples are
At Alternative to Meds Center, many therapeutic aids are available to help ease the tapering process. Some examples are 







